DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TPMS Function
The TPMS uses four valve stem-mounted sensors to monitor tire pressure. These sensors wirelessly transmit tire pressure data to the Remote Transceiver Module (RTM). The RTM is a radio signal receiver which collects the tire pressure data and sends the information to the Body Control Module (BCM) along a Local Interconnect Network (LIN). All TPMS functions are controlled by the BCM. The BCM compares the tire pressure data sent by the RTM with a programmed tire pressure. This programmed pressure is specified on the VC label and cannot be changed. If the actual tire pressure is less than the programmed tire pressure, the BCM sends a low tire pressure message to the GWM along the HS-CAN1. The Gateway Module (GWM) then sends this message to the IPC along the HS-CAN3. The IPC responds by illuminating the TPMS warning indicator and displaying a low tire pressure message in the message center. The TPMS sensors are trained (calibrated) to the BCM which records the unique identifier for each TPMS sensor and records the location of each sensor based on the calibration order. The BCM sends messages to the RTM by first sending the information along the HS-CAN1 to the GWM which then sends the information to the RTM along the MS-CAN.
The diagnostic scan tool is useful in diagnosing TPMS concerns and may be used to verify the accuracy of the tire pressure data transmitted by the TPMS sensors. This is accomplished by comparing the BCM tire pressure PID data to the actual tire pressure using a digital tire pressure gauge. It is not necessary to train the sensors after a tire rotation on vehicles with the same front and rear tire pressures however, the BCM cannot recognize the sensor identifiers have been moved to different positions and retains the original position information for each sensor.
Wheel Rotation and Sensor Training Techniques
Training known good sensors from another vehicle can help determine whether the concern is with a sensor or the RTM. This technique cannot help determine whether the concern is due to RFI as some RFI source could be preventing the RTM from receiving the tire pressure status from the known good sensors as well as the original sensors. If the RTM in the suspect vehicle cannot train any of the original sensors and, likewise, cannot train known good sensors from another vehicle, then the concern is with the module or RFI and not with the original sensors. The original sensors should not be replaced. If a sensor in a certain location has caused several events, yet the sensor trains and seems to operate normally, moving that particular wheel to a different location on the vehicle is a good way to isolate the concern to a certain sensor/wheel location. Rotate the wheels and road test the vehicle. This can be done in an attempt to replicate the concern and help determine if the concern followed the sensor or remained in the original sensor location. If the vehicle has been stationary for more than 30 minutes, the sensors go into a "sleep mode" to conserve battery power and need to be "woken up" so they transmit the latest tire pressure information to the RTM.
Training Sensors in a Different Order
If the first sensor fails the TPMS training procedure, the BCM aborts the entire procedure. Starting the training procedure at a different wheel is a technique that can be used to determine if the remaining sensors can train to the module. This can help save time determining if one sensor is damaged, other sensors are having concerns or the BCM is experiencing training difficulties with a certain TPMS sensor location.
TPMS ACTIVATION
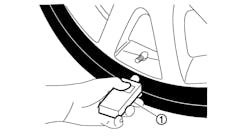
1) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
2) Position the special tool against the Left Front (LF) tire sidewall at the tire valve stem.
3) Press the test button on the special tool to activate the sensor. Activate the sensor at least two times.
4) Repeat these steps for the remaining tires.
TIRE PRESSURE SENSOR REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
DISASSEMBLY
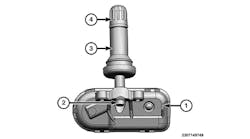
Failure to follow the instructions below may result in damage to the TPMS. The TPMS sensor is mounted to the valve stem. Removal of the valve stem requires demounting the tire from the wheel and removal of the TPMS sensor.
Use only a digital tire pressure gauge any time tire pressures are measured to ensure accurate values are obtained.
1) Remove the wheel and tire. (The valve stem is connected to the TPMS sensor. Do not pull the valve stem from the wheel, or damage to the sensor will occur.) If a new TPMS sensor is being installed, remove and discard the valve stem-to-sensor screw and the sensor.
2) Remove the valve stem core and fully deflate the tire.
Do not allow the tire beads to move beyond the wheel mid-plane (middle of the wheel) when separating the beads from the wheels; damage to the TPMS sensor may occur.
Tire and valve stem position is critical to prevent damage to the TPMS sensor when using a paddle-type bead separator. Some machines may have a nylon roller bead separator at the 12 o'clock position instead of the paddle-type bead separator at the 3 o'clock position.
3) For a paddle-type tire machine, position the valve stem at the 12 o'clock or 6 o'clock position and the paddle at the 3 o'clock position. For a roller-type tire machine, align the valve stem with the roller at any position.
If bead separation is difficult to achieve using the nylon roller bead separators due to high anchoring force between the tire and the wheel; the paddle-type bead separator may be a more effective method.
Index-mark the valve stem and wheel weight positions on the tire.
4) Place the wheel and tire assembly on the turntable of the tire machine with the valve stem at the 11:30 position and the machine arm at the 12 o'clock position and demount the outer bead from the wheel.
5) Reset the wheel and tire assembly on the turntable of the tire machine with the valve stem at the 11:30 position and the machine arm at the 12 o'clock position and demount the inner bead from the wheel.
A new valve stem must be installed whenever a new tire or wheel is installed.
6) Remove and discard the TPMS sensor-to-valve stem screw. Separate the TPMS sensor from the valve stem.
Use care not to damage the wheel surface when removing the valve stem. When installing a new wheel, always install a new valve stem and sensor screw. Reuse the TPMS sensor from the previous wheel if possible. The TPMS will not have to be trained if the sensor is reused. If the TPMS sensor is being reused, inspect the TPMS sensor for damage and install a new sensor as necessary.
7) Discard the specified component. Follow local disposal regulations. Use the General Equipment: Wooden Block.
To prevent TPMS sensor and valve stem damage, the valve stem must be installed onto the TPMS sensor and then installed into the wheel as an assembly.
8) Position the new valve stem onto the TPMS sensor and install the new screw.
ASSEMBLY
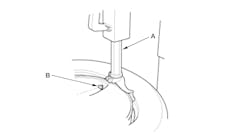
It is important to pull the valve stem and TPMS sensor assembly through the wheel rim hole in a direction parallel to the valve stem hole axis. If the assembly is pulled through at an angle, damage to the valve stem and sensor assembly may occur.
Use care not to damage the wheel surface when installing the valve stem and TPMS sensor assembly.
Lubricate the valve stem with soapy water and install the valve stem and TPMS sensor assembly into the wheel using a block of wood and a suitable valve stem installer.
1) Use the General Equipment: Wooden Block
Lubricate the tire beads using a suitable fast-drying, corrosion-inhibiting tire bead lubricant. Do not mount the tire at this time.
2) Position the wheel on the turntable of the tire machine, then lubricate and position the bottom bead of the tire on the wheel.
3) Position the wheel to align the valve stem with the machine arm, at the 6 o'clock position, and mount the bottom bead of the tire
4) Reposition the wheel to align the valve stem with the machine arm at the 6 o'clock position, and mount the top bead of the tire.
Use only the digital tire pressure gauge any time tire pressures are measured to be sure that accurate values are obtained.
Proceed to the next step if the tire beads do not seat at the specified inflation pressure.
5) Inflate the tire to the pressure specified on the VC label located on the driver door or door pillar.
If there is a need to exceed the maximum pressure indicated on the sidewall of the tire in order to seat the beads, follow all steps listed below. Failure to follow these steps may result in serious personal injury.
- Relubricate the tire bead and wheel bead seat area
- Install a remote valve and pressure gauge.
- Wear eye and ear protection and stand at a minimum of 12 feet away from the wheel and tire assembly.
- Inflate the tire using the remote valve and tire gauge until the beads have seated or until the pressure gauge is 20 psi more than maximum inflation pressure on tire sidewall. If beads have not seated, deflate the tire and proceed to the next step.
- Place the wheel and tire assembly in an OSHA-approved tire safety cage.
- Inflate the tire using the remote valve and pressure gauge until the beads have seated or until the pressure gauge is 40 psi more than maximum inflation pressure on the tire sidewall. Do not exceed 40 psi above the maximum pressure on tire sidewall. Install a new tire if the beads do not seat at this pressure.
6) Install the wheel and tire.
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
Item Nm lb-in
Valve stem-to-TPMS sensor screw 1.5 13
Wheel nuts 135 100