DESCRIPTION and OPERATION
The tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) monitors the pressure of each tire and warns the driver when either a low tire pressure condition or TPMS malfunction exists. The TPMS will display the conditions through the Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC). There are two TPMS systems available for this vehicle, a Base and a Premium system. The Base systems only uses a TPMS telltale (audible chime), and non-positional text messages to indicate low pressure or system fault conditions. The Premium system uses all the available functions of the Base system as well as the Electronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC) located in the IPC to display the actual tire pressure values (or dashes when a sensor error has occurred) for each of the active road tires in the correct vehicle position. Various text messages when prompted by the system will also be displayed in the vehicle information display. After a tire rotation, the system auto locates the tire location and displays its pressure readings at the proper location in the EVIC.
When tire pressure is 7-8 psi below the specification listed on the label, the system emits the TPMS chime, illuminates the low tire pressure warning light as well as displays the pressure of the four active tires in the EVIC display when equipped with the Premium system. If a system fault is detected, the warning light will flash for 75 seconds, then remain on continuously. Dashes will take the place of the pressure reading if a sensor is not correctly operating. A five-sensor system is available for vehicles with a full-size spare wheel (in markets where provided). The TPMS system uses four or five tire pressure sensors designed for mounting in place of a traditional tire valve. The tire pressure sensor includes a stem that looks similar to a standard stem. The sensor body, located at the bottom of the stem contains a sensor, a processor, a transmitter/receiver, and a non-removable coin battery that lasts up to ten years. If the battery fails, the sensor must be replaced.
The horn will chirp once when the correct recommended cold placard pressure value is reached. The horn will chirp three times if the tire inflation pressure has exceeded the recommended value by a preset percentage and will continue to chirp three times every time the measured tire pressure increases by a preset percentage and the alert mute timer has expired. The horn will also chirp three times if the tire is deflated below the recommended cold placard pressure by a preset percentage and will continue to chirp three times every time the measured tire pressure decreases by a preset percentage and the alert mute timer has expired. The TFA system shall include an alert mute time between horn chirp alerts. The mute timer will begin immediately after any user alert is provided. Any further user alert cannot be provided during this mute time.
When the TPMS sensor detects that the vehicle is not in motion and that the pressure in the tire has changed from the last transmitted pressure value by a pressure value as specified in the sensor performance standard, the sensor will enter TFA mode. The TPMS sensor can enter TFA mode on either an inflation or deflation pressure change since the last transmitted pressure value. The sensor will transmit an environment data code once it has entered TFA mode to indicate to the receiver module that the sensor is in TFA mode. Refer to the TPMS sensor performance standard for the environment data code that indicates the sensor state. Once in TFA mode the sensor will monitor and transmit the pressure at a rate as specified in the sensor performance standard.
INSTRUMENT PANEL CLUSTER (IPC)
The Radio Frequency Hub (RFH) controls the TPMS indicator lamp bulb check through the tire pressure indication request. The bulb check is repeated at every transition of the commanded ignition switch status message event from OFF to ON. With a Premium TPMS, the IPC will display the pressure values transmitted for all four active sensors in vehicle position. An under-inflation condition will cause a text message to be displayed, an audible chime to sound and the tire pressure indicator lamp to illuminate. The audible chime will occur once per ignition cycle for the first "warning" detected. When an under-inflation condition is detected and sent in the tire pressure indication request message, the IPC will turn the TPMS indicator lamp ON and the lamp will remain ON when the ignition is in the ON/RUN position until the low tire pressure condition is corrected. When an under-inflation condition occurs for a Base TPMS, a low tire pressure text message will be displayed. When an under-inflation condition occurs for a Premium TPMS, a low tire pressure text message may be displayed or low tire pressure text messages including the location of the low tire may be displayed. In the IPC the pressure value of the tire that is low will change to a different color until the low-pressure condition is corrected. For monotone display screens, the pressure value of the tire that is low will be highlighted until the low-pressure condition is corrected. The tire pressure display screen will remain displayed indefinitely or until another display screen is selected. If more than one low tire pressure condition exists, the pressure value of each tire that is low will change colors or will be highlighted.
Controller Area Network (CAN-C) inputs: TPMS chime request; Tire pressure indication request; TPMS localization status; TPMS hazard flash; Tire location for each wheel; Tire pressure for each wheel; Front tire maximum load inflation pressure; Rear tire maximum load inflation pressure; Base TPMS present; Premium TPMS present; and TPMS configuration.
RADIO FREQUENCY HUB (RFH)
The RFH is an integrated receiver (base station) in the vehicle that interfaces with the Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) fob using both RF Radio Frequency and LF (Low Frequency). The RFH contains the controlling logic for the Passive Entry Keyless Go (PEKG) feature, and the Keyless Ignition Node (KIN) lighting. The RFH communicates on the CAN-C bus as well as a dedicated K-line with the KIN. The RFH is also hard wired to the vehicle's door handles and multiple LF antennas for purposes of providing PEKG functionality. The RFH is connected to a fused B(+) circuit and has a path to a clean ground at all times. These connections allow it to remain functional regardless of the ignition switch status. Any input to the RFH that controls a vehicle system function that does not require that the ignition switch status be ON such as depressing a button on an RKE or FOB transmitter, prompts the RFH to wake up and transmit on the CAN-C data bus.
The RFH receives the following:
CAN-C Inputs: Vehicle configuration data; Transfer case status; Ambient Air Pressure; Current gear selected; Wheel pulse counter from each wheel; Vehicle speed; Odometer; System voltage; Commanded ignition switch status; Ignition run active for remote start; Averaged ambient temperature; and Month, day, and year.
RF Inputs: Right front tire pressure sensor; Right rear tire pressure sensor; Left front tire pressure sensor; Left rear tire pressure sensor.
The RFH provides the following:
CAN-C Outputs: TPMS chime request; Tire pressure indication request; TPMS localization status; TPMS hazard flash; Tire location for each wheel; Tire pressure for each wheel; and TPM horn chirp.
CAN-IHS Outputs: TFA status enabled or disabled.
TIRE PRESSURE SENSOR
One tire pressure sensor is mounted to a valve stem in each wheel in place of the traditional tire valve stem. Each sensor has an internal battery that lasts up to 10 years. The battery is not serviceable. At the time of battery failure, the sensor must be replaced. The TPMS system operates on a radio frequency of 433 MHz. The tire pressure sensor valve stem looks similar to a standard valve stem with the tire mounted on the wheel. To visually identify a tire pressure sensor/valve stem, the valve stem cap is longer than a standard valve stem. The TPMS sensors are designed for original style factory wheels. It is not recommended to install a tire pressure sensor in an aftermarket wheel. (This could cause sealing and system performance issues.)
The valve stem caps and cores used are specifically designed for the tire pressure monitoring sensors. Although similar to standard valve stem caps and cores, they are different. The valve stem cap has a special seal inside to keep out moisture and corrosion. The valve stem core has a special nickel coating to protect from corrosion. The wireless sensors transmit tire pressure information at a frequency of 433 MHz. The tire pressure sensors send a tire pressure sensor value every 64 seconds when the vehicle is in motion and approximately every 13 hours when the vehicle is not in motion. The sensors also transmit a unique ID code to differentiate the sensors from those on nearby vehicles. When a sensor is installed in a tire on the vehicle, the RFH can automatically identify the sensor and its location during the first ensuing drive cycle. Identification will take approximately 20 minutes, but the speed of the vehicle must exceed 15 mph. The Kit, TPM/RKE ANALYZER 2046300080 can also be used to program the new sensor identification number in the RFH. The Tire pressure sensor provides the following:
RF Outputs: Right Front tire pressure sensor; Right Rear tire pressure sensor; Left Front tire pressure sensor; and Left Rear tire pressure sensor.
MEMORIZING THE TIRE PRESSURE SENSOR ID
The RFH is used to receive the radio signals from the tire pressure sensors and sends the relevant values to the other modules through the Controller Area Network-Chassis (CAN-C) and Controller Area Network-Interior High Speed (CAN-IHS). The RFH module identifies the sensor position, receives the sensor data, compares the pressure data with the standard pressure values stored in the non-volatile memory, determines whether there is a problem in the tire pressure and stores the warnings regarding tire pressure and system faults. The RFH uses the RF Data from the TPMS sensor and the vehicle traction control module wheel speed data to determine the location of each tire pressure sensor. When a sensor is installed in a tire on the vehicle, the RFH can automatically identify the sensor and its location during the first ensuing drive cycle. Identification will take approximately 20 minutes but the speed of the vehicle must exceed 15 mph. The Kit, TPM/RKE ANALYZER 2046300080 can also be used to program the new sensor identification number in the RFH module. The sensor identifications (IDs) can also be programmed using a Scan Tool.
Some models of the vehicle are equipped with Tire Fill Alert (TFA) system. It is designed to provide feedback to the customer, while inflating one or more of the vehicle's tires. The TFA system will only support inflating one tire at a time. The system is intended to inform the customer that they have reached the correct manufacturer's recommended cold placard pressure inflation value. The system will provide a visual alert, through use of the vehicle's hazard flasher lights, to inform the customer that they have entered the Tire Fill Alert mode. Once in Tire Fill Alert mode, the system will provide an audible alert to the customer through use of the vehicle's horn. When the TPMS sensor detects the vehicle is not in motion and detects that the pressure in the tire has changed from the last transmitted pressure value by a pressure value as specified in the TPMS sensor performance standard, the sensor will enter TFA mode. The sensor can enter TFA mode on either an inflation or deflation pressure change from the last transmitted pressure value.
TIRE PRESSURE SENSOR REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
REMOVAL
The tire pressure sensor, the valve stem, and all valve stem components including the cap and the valve core can be serviced and replaced individually.
When demounting or mounting the tire on the wheel, follow the tire changer manufacturer’s instructions while paying special attention to avoid damaging the pressure sensor.
- Raise and support the vehicle.
- Remove tire and wheel assembly and dismount the tire from the wheel.
Replace the valve stem (3) assembly with each tire change or when the tire is removed from the wheel.
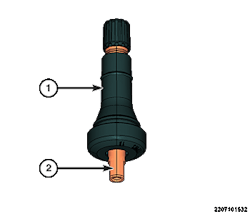
- To remove the sensor (1) from the valve stem (3), remove the tire pressure sensor screw (2) as shown in Fig. 1.
- Remove the valve stem (3) from the wheel.
INSTALLATION
Any time a sensor is to be reinstalled in a wheel, a new valve stem assembly must be installed to ensure airtight sealing.
When installing a NEW valve stem assembly (3), do not install it with the sensor (1) attached.
When installing a new valve stem, soapy water solution should be used for proper installation to the wheel.
- Wipe the area clean around valve stem mounting hole in wheel. Verify the surface of wheel is not damaged.
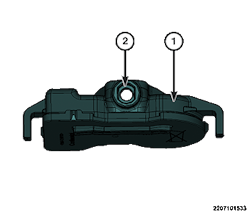
- Position the valve stem (1) into the wheel mounting hole with the flats (2) at a 90-degree angle to the wheels lip, then pull through to seat with a standard valve stem installation tool, as shown in Fig. 2.
- Install the sensor (1) to the valve stem by aligning the flats in the sensor to the flats (2) on the valve stem.
When demounting or mounting the tire on the wheel, follow the tire changer manufacturer’s instructions while paying special attention to avoid damaging the pressure sensor.
- Install the tire pressure sensor to the valve stem, then install and securely tighten the tire pressure sensor screw (2).
- Mount the tire on the wheel and install tire and wheel assembly on the vehicle.
- Adjust air pressure to that listed on tire inflation pressure placard provided with vehicle (usually applied to driver's side B-pillar). Verify the original style valve stem cap is securely installed to keep moisture out of sensor.
- Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
- Perform one of the following to make the system learn the new sensor ID:
Use the Kit, TPM/RKE ANALYZER 2046300080, with a scan tool to program the Radio Frequency (RF) hub with the tire pressure sensor ID. This is part of the TPM diagnostic verification test.
Drive the vehicle for a minimum of 20 minutes while maintaining a continuous speed above 20 mph. During this time, the system will learn the new sensor ID.
If a sensor cannot be trained, refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.